

Carbohydrazide
Alias: carbazide; 1, 3-diaminourea; Carbohydrazide; Dihydrazine carbonate; 4-amino-hemiuret; Dihydrazide carbonate; saccharohydrazine
CAS: 497-18-7
Molecular formula: CH6N4O
Molecular weight: 90.08
Molecular structure formula: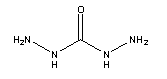
Appearance: white thin short columnar crystal
Melting point: 150 ~ 155℃.
Content: 99%; Chemical analysis
Free hydrazine: ≤500PPM
Solubility: insoluble in ethanol, easily soluble in water, dissolve heat.
Nitrogen content: 62.17%
Acid-base: 1% aqueous solution, p H=7.4
Explosive: without any explosive, transport, storage and use is relatively safe
Chemical properties: dissolve and absorb heat. Nitrogen content of 62.18%,1% aqueous solution PH=7.4, no moisture absorption, has a very strong reducibility. It reacts with hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, phosphoric acid and nitric acid to form salts. The resulting chlorides are highly soluble in water; Sulfate and oxalate are slightly soluble in water; Phosphate and nitrate cannot be crystallized. In the presence of nitrite, carbonyl hydrazine is converted into a highly explosive compound called carbonyl azide CO(N3)2. Carbylhydrazide will decompose when an aqueous solution is co-heated with an acid
Toxicity: intravenously, the LD50 for mice is 120mg/kg for internal administration, and the LD50 for mice is 167mg/kg
Uses: Widely used in the production of drugs, herbicides, plant growth regulators, dyes and so on
(1) Carbonyl hydrazine is a derivative of hydrazine, with strong reductibility, can be used as an intermediate for the manufacture of energetic materials, and can also be directly used as a component of explosive and propellant.
(2) Preservative of refinery equipment, which can be used as deaerator of boiler water treatment agent.
(3) Chemical fiber industry as a crosslinking agent for elastic fibers.
(4) As chemical raw materials and chemical intermediates, it is widely used in medicine, herbicides, plant growth regulators, dyes and other industries.